Defaults
Reduce friction during resource creation by applying defaults that are both transparent and useful to the user.
Reduce friction during resource creation by applying defaults that are both transparent and useful to the user.
Reduce friction
Use well-chosen defaults in as many fields as possible to allow users to quickly set up a resource with minimal configuration.
When defaults apply
Defaults typically apply at creation or edit time. Dynamic configurations reflect system-managed behavior and should be surfaced transparently.
Provide visibility on API defaults
Users should understand what happens when the field is left blank and the API applies a value. Make this outcome clear by either showing the value in the field or explaining the behavior when the field is left blank.
Values pre-populated by the service before creation to guide user setup. Examples include recommendations, account preferences, or prior choices. For example, pre-selecting an encryption key.
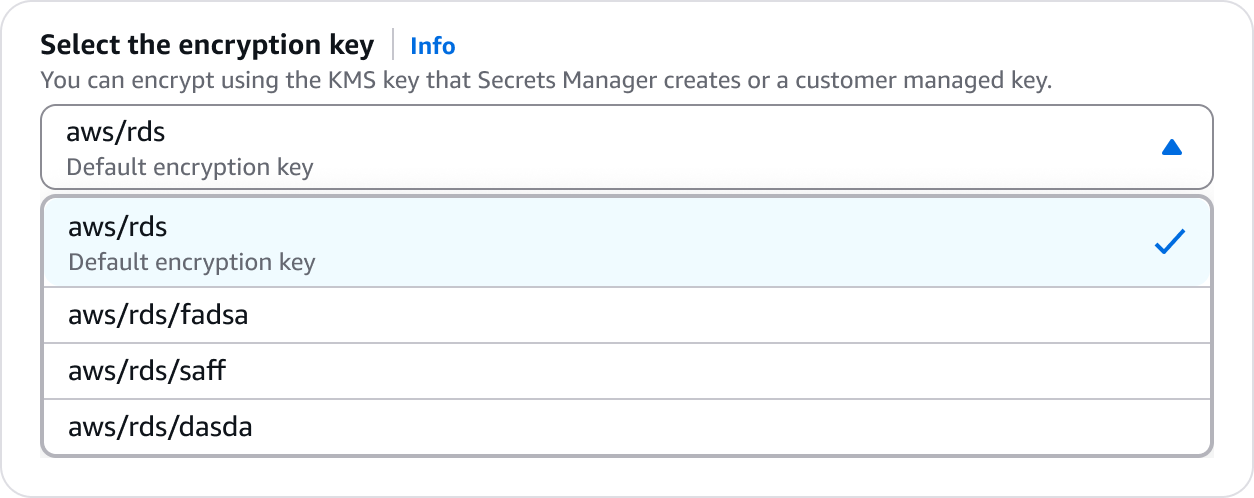

Populate and pre-select with the fixed value.
Provide additional details of how the value is defined.
Values applied by a service backend when a field is left empty or no selection is made. These may be pre-filled or pre-selected to reflect what will be applied if the user takes no action. Make users aware of this behavior either by showing the fixed value or by indicating that the value will be determined on creation or runtime.
There are three types:
Known values pre-filled to show the user what will be applied. For example, pre-populating an input with a volume initialisation rate with the value shown in the constraint text.
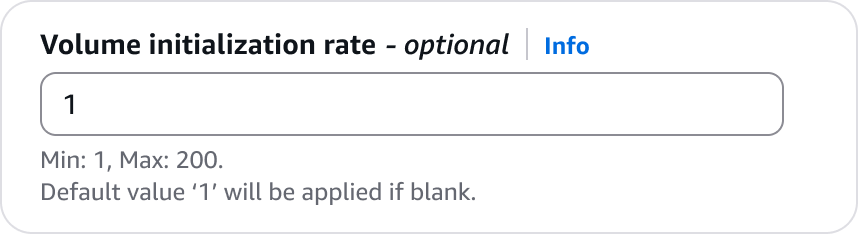
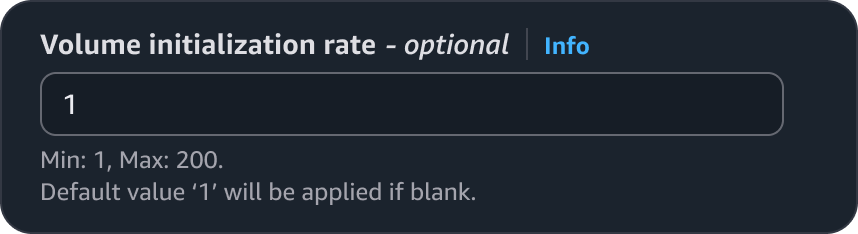
Populate with the fixed value.
Include the value so the user knows what value will be applied if the input is cleared.
Values determined at creation time. For example, an availability zone that is defined on creation.
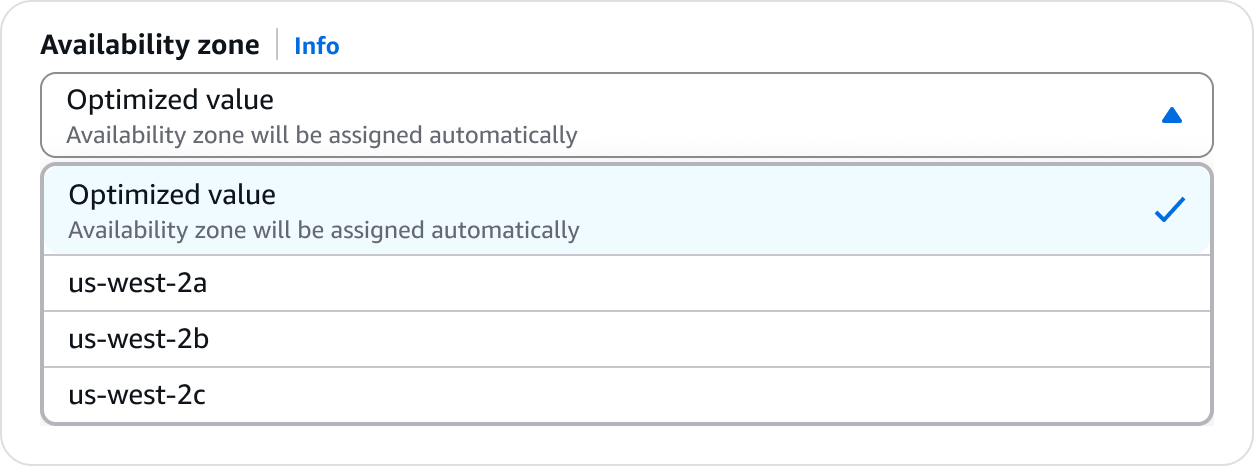
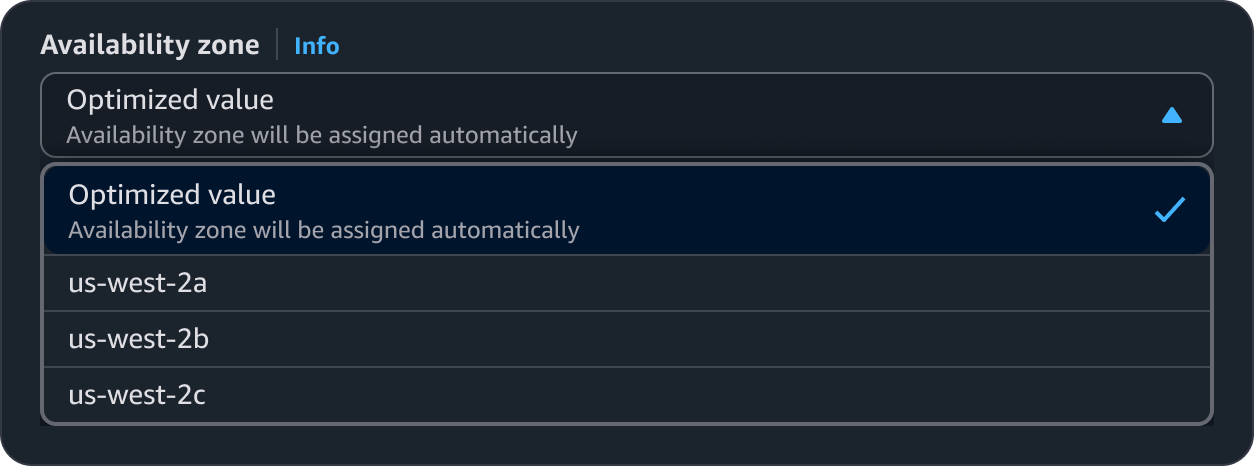
Provide details on the value and be as descriptive as possible.
Provide additional details on how the value will be determined.
Provide help panel content to explain how the value is defined if this can not be covered in the description only.
Values determined and updated at runtime based on system conditions or configuration logic. For example, an Auto Scaling group adjusts its desired capacity to maintain a target CPU utilization of 50%. These values are typically not shown in the UI as a selection, and the system manages them dynamically after creation.
Use sentence case, but continue to capitalize proper nouns and brand names correctly in context.
Use end punctuation, except in headers and buttons. Don’t use exclamation points.
Use present-tense verbs and active voice.
Don't use please, thank you, ellipsis (...), ampersand (&), e.g., i.e., or etc. in writing.
Avoid directional language.
For example: use previous not above, use following not below.
Use device-independent language.
For example: use choose or select not click.
Clearly describe what the API will do if the user takes no action.
Example: “A default value of ‘1’ will be applied if left blank.”
When a value is pre-selected, explain what the API will apply and when.
Example: “Availability Zone will be assigned automatically on creation.”
Match the timing language to the type of API default, for example:
Automatic: “assigned automatically on creation.”
Dynamic: “adjusted automatically at runtime.”
Avoid redundancy between the option label and description.
If the label already implies automation (“Optimized”), the description should clarify what will happen, not repeat it.